EV tax incentives are driving the global shift towards electric vehicles. These financial incentives are playing a crucial role in shaping the automotive industry and encouraging wider adoption of electric vehicles. From government subsidies to tax credits, various programs are in place to make EVs more affordable and accessible.
This analysis explores the multifaceted nature of EV tax incentives, delving into their design, effectiveness, and impact on the market. We examine the historical trends, global comparisons, and potential challenges associated with these policies. Furthermore, we will assess the economic implications, public perception, and future directions of EV tax incentives, offering a comprehensive understanding of their role in promoting sustainable transportation.
Overview of EV Tax Incentives
Electric vehicle (EV) tax incentives are a crucial component of global efforts to accelerate the adoption of sustainable transportation. These incentives, which vary significantly across countries, aim to reduce the financial burden of purchasing EVs, making them more competitive with traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. The effectiveness of these programs is often assessed by their impact on sales figures, charging infrastructure development, and overall emissions reductions.
Existing EV Tax Incentives Globally
Governments worldwide implement a range of incentives to encourage EV adoption. These commonly include tax credits, rebates, and exemptions from certain taxes, such as sales tax or registration fees. Some programs also offer subsidies for charging infrastructure, incentivizing the development of a robust network for EV owners. These programs are frequently adjusted to align with government policies and market demands.
Types of Vehicles Eligible for Incentives
Eligibility criteria for EV tax incentives often differentiate between different types of electric vehicles. Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) typically receive the most substantial support. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) often qualify for incentives, but generally receive less favorable treatment than BEVs. The criteria may also consider the vehicle’s battery capacity, range, and other performance specifications.
Historical Trends and Evolution of Incentives
The development of EV tax incentives mirrors the evolution of EV technology and market demand. Early incentives were often modest and focused on specific regions or countries. As EV technology matured and consumer interest increased, incentives became more comprehensive and substantial. The ongoing trend involves greater standardization and harmonization of policies across different regions. The historical data reflects the growing commitment to reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable transportation.
Comparison of Incentive Effectiveness Across Regions
The effectiveness of EV tax incentives varies considerably across countries and regions. Factors such as consumer preferences, charging infrastructure availability, and government commitment to sustainable development all play a role in determining the success of these programs. Success is often measured by observing increases in EV sales, the growth of charging stations, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Table of EV Tax Incentives by Country/Region
| Country/Region | Type of Incentive | Amount (Approximate) | Vehicle Type Eligibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Tax Credit | $7,500 (or more, depending on the manufacturer and vehicle) | BEVs, PHEVs |
| China | Subsidies, Tax Exemptions | Variable, often significant | BEVs, PHEVs |
| Germany | Tax Deductions, Subsidies | Variable, often substantial for high-battery capacity EVs | BEVs, PHEVs |
| France | Tax Credits, Rebates | Variable, dependent on the vehicle’s battery capacity | BEVs, PHEVs |
| Norway | Extensive incentives, including reduced taxes and import duties | High amounts for many BEVs | BEVs, PHEVs |
Note: The amounts listed are approximate and may vary based on specific vehicle models and eligibility criteria. These are examples, and actual incentives can be significantly more or less than these values.
Impact on the EV Market
Tax incentives play a crucial role in shaping the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). Their impact extends beyond simply encouraging purchases; they influence broader market trends, driving innovation and potentially reshaping the automotive landscape. Understanding this influence is vital for assessing the long-term viability and growth trajectory of the EV sector.Incentives directly affect consumer purchasing decisions, motivating individuals to choose EVs over conventional vehicles.
This impact, often measurable in sales figures, can be further analyzed by correlating incentive levels with adoption rates. By understanding these relationships, we can gain insights into the effectiveness of various incentive structures and their potential to accelerate EV market penetration.
Effect on EV Sales Figures
Government incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, significantly impact EV sales. Studies have shown a clear correlation between the level of incentives and the number of EVs sold. Increased incentives often lead to a surge in sales, as consumers are more likely to purchase EVs when the financial benefits are substantial. This effect is particularly noticeable in regions where the cost of an EV is relatively high compared to a comparable gasoline-powered vehicle.
Correlation Between Incentive Levels and EV Adoption Rates
A strong correlation exists between the level of tax incentives and the rate of EV adoption. Higher incentives tend to correlate with higher adoption rates, indicating a direct relationship. This correlation suggests that incentives are a key driver in encouraging consumers to switch to EVs. Furthermore, these correlations can vary across different market segments and demographics, highlighting the need for tailored incentive strategies.
Influence on Consumer Purchasing Decisions
Tax incentives are a significant factor influencing consumer decisions to purchase EVs. The financial benefits offered by incentives often outweigh the higher initial cost of EVs compared to traditional vehicles. Consumers frequently consider the total cost of ownership when making purchasing decisions, and incentives directly reduce the overall cost, thus increasing the appeal of EVs.
Role of Incentives in Shaping the Future of the Automotive Industry
Tax incentives are pivotal in shaping the future of the automotive industry. They foster a shift towards cleaner transportation, accelerating the transition to electric mobility. By incentivizing EV adoption, governments and policymakers can encourage innovation and investment in the EV sector, leading to the development of more efficient and affordable EV technologies. This ultimately propels the automotive industry toward a sustainable future.
Comparison of EV Sales Data (Hypothetical Example – Europe)
| Year | EV Sales (with Incentives) | EV Sales (without Incentives) |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 500,000 | 250,000 |
| 2023 | 600,000 | 300,000 |
| 2024 | 750,000 | 400,000 |
Note: This table presents hypothetical data to illustrate the impact of incentives. Actual figures may vary based on specific market conditions and policy implementations.
Incentive Design and Effectiveness
Designing effective EV tax incentives is crucial for accelerating the transition to electric vehicles. These programs need to balance the desire to encourage adoption with the practicalities of budget constraints and potential market distortions. Careful consideration of eligibility criteria, program design, and the evaluation of past successes and failures is essential for maximizing impact.Incentive programs vary significantly across jurisdictions, impacting the adoption rate and overall market penetration of EVs.
Understanding the intricacies of these programs, from the specific criteria for eligibility to the different incentive structures, is vital for evaluating their effectiveness. Comparative analyses of different programs reveal important lessons for future design and implementation.
Eligibility Criteria for Incentives
Eligibility criteria are often based on factors like vehicle specifications, battery capacity, and the manufacturer’s production location. These specifications are typically intended to encourage the adoption of more environmentally friendly and technologically advanced EVs. Incentives are designed to target specific vehicle types, promoting broader market adoption. Examples include incentives for EVs with higher battery capacities or those made by domestic manufacturers, aiming to support domestic production and technological advancements.
Incentive Program Design
Different incentive programs employ various strategies. Some offer upfront rebates, while others provide tax credits. Some programs focus on specific vehicle classes (e.g., passenger cars, trucks), or may offer different tiers of incentives based on the battery capacity of the vehicle.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Programs
Numerous countries and regions have implemented EV tax incentive programs. The success of these programs varies greatly, depending on the specific design and the prevailing market conditions. Successful programs often see a significant increase in EV sales in the targeted market segment, demonstrating the positive impact of financial incentives. Conversely, unsuccessful programs may fail to generate substantial market changes, possibly due to poor design or insufficient public awareness.
For instance, some programs may not adequately incentivize the purchase of more efficient vehicles.
Comparison of Incentive Structures
The effectiveness of different incentive structures is subject to evaluation. Direct rebates are often easier to understand and administer, while tax credits may be more complex but offer potential benefits through broader societal impact. The effectiveness of a specific incentive structure depends on the local market conditions and the specific goals of the program.
Table: Comparison of Incentive Structures
| Incentive Structure | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Rebates | Easy to understand and implement, immediate impact on purchase decisions. | May not provide long-term financial benefits, potential for reduced government revenue. |
| Tax Credits | Potential for wider societal benefits through tax relief, long-term financial benefits. | More complex to implement and administer, potential for reduced government revenue if not well designed. |
| Mileage-Based Incentives | Encourages the adoption of more efficient EVs. | May not be well-suited for all types of vehicles or markets, potentially difficult to accurately track and measure. |
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While EV tax incentives are a crucial tool for promoting electric vehicle adoption, their implementation comes with potential drawbacks. Careful consideration of these challenges is essential to ensure the effectiveness and sustainability of such programs. These drawbacks, coupled with implementation hurdles, must be addressed to maximize the positive impact on the market and avoid unintended consequences.
Potential Drawbacks of Tax Incentives
Tax incentives, while intended to stimulate demand, can sometimes create unintended market distortions. For instance, they might incentivize purchases over and above what a market-driven approach would suggest. This can result in an oversupply of EVs in certain segments, potentially impacting existing manufacturers and the long-term viability of the market. Furthermore, the design of incentives can inadvertently create disincentives for other environmentally friendly solutions, such as energy-efficient vehicles that don’t qualify for the same tax breaks.
A nuanced understanding of the broader market context is critical to mitigating such risks.
Challenges in Implementing and Managing Incentive Programs
The administration of EV tax incentive programs can be complex, demanding substantial resources for verification, monitoring, and enforcement. Difficulties in accurately determining eligibility and verifying compliance can lead to program abuse and administrative burdens. The bureaucratic processes involved in claim processing and auditing can also deter participation and hinder the smooth rollout of the initiative. Moreover, maintaining consistent and updated guidelines to reflect evolving technologies and market conditions is a constant challenge.
Potential for Fraud or Abuse
A significant concern with any incentive program is the potential for fraud or abuse. Individuals or businesses might attempt to exploit loopholes in the rules to claim incentives fraudulently. This could range from misrepresenting vehicle characteristics to submitting false documentation. Effective monitoring and verification mechanisms, coupled with robust penalties for fraud, are necessary to deter and address such instances.
Examples of such fraudulent activities exist in other tax incentive programs, highlighting the importance of proactive measures.
Limitations of Relying Solely on Incentives
Incentives are merely a catalyst; they cannot be the sole driver of widespread EV adoption. Consumer preferences, charging infrastructure availability, and the overall cost-effectiveness of EVs play crucial roles in the uptake of this technology. Over-reliance on incentives could lead to a temporary surge in sales that doesn’t translate into sustained market growth. Long-term success necessitates a holistic approach that addresses the entire EV ecosystem, including infrastructure development and consumer education.
Table: Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
| Potential Challenge | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Market distortions due to excessive incentives | Design incentives that are targeted and proportionate to the environmental benefit. Continuously monitor market trends and adjust incentives as needed. |
| Implementation and management complexities | Invest in robust administrative systems and personnel. Establish clear eligibility criteria and streamline verification processes. Develop user-friendly claim submission portals. |
| Fraud and abuse | Implement robust verification procedures and fraud detection systems. Enhance transparency in the incentive program’s operation. Impose substantial penalties for fraudulent activities. |
| Over-reliance on incentives | Develop a comprehensive strategy that addresses the entire EV ecosystem, including infrastructure development and consumer education. Encourage private sector investment in charging infrastructure. |
Future Trends in EV Tax Incentives
The landscape of electric vehicle (EV) tax incentives is dynamic and likely to evolve significantly in the coming years. Government policies are frequently adjusted in response to market changes, technological advancements, and evolving societal needs. Predicting the precise form of these future incentives requires careful consideration of various factors.
Predicted Evolution of EV Tax Incentives
A range of factors could influence the future trajectory of EV tax incentives. Technological advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure could lead to increased adoption of EVs, potentially reducing the need for substantial incentives. Conversely, persistent concerns about environmental sustainability and the transition to a low-carbon economy could maintain or even bolster support for EV incentives. Government responses to economic conditions and public pressure also play a significant role.
Potential Policy Changes and Reforms
Several policy changes are possible. Incentives might be shifted towards specific vehicle types, such as commercial EVs or EVs with advanced features. The criteria for eligibility for incentives could be refined, potentially excluding higher-priced models in favor of more accessible options. Incentives could be tied to the manufacturing location of the EV, promoting domestic production. Furthermore, incentives could become tied to specific charging infrastructure investments, creating a positive feedback loop.
Potential Emergence of New Incentive Types
New incentive types might emerge. For example, incentives could be designed to encourage the adoption of EV charging infrastructure by homeowners and businesses. These incentives could take the form of rebates or tax credits for installing charging stations. Furthermore, incentives might be introduced to promote the recycling of EV batteries, fostering a circular economy for EV components.
Finally, incentives could be focused on reducing the environmental impact of EV production, such as tax credits for using sustainable materials.
Implications of International Cooperation on EV Tax Incentives
International cooperation is increasingly important in the EV sector. Harmonized EV tax incentives across borders could encourage greater investment and accelerate the global transition to EVs. This cooperation could lead to more effective and efficient policies, reducing barriers to cross-border trade and promoting innovation. Furthermore, international agreements on EV standards and regulations could further streamline the development and adoption of EVs.
Potential Future Trends Table
| Year | Predicted Change | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | Expansion of incentives to include charging infrastructure installations | Increased adoption of home and public charging stations, potentially driving down the cost of EV ownership. |
| 2027 | Focus on incentivizing EVs manufactured domestically | Boost to domestic EV manufacturing, job creation, and reduced reliance on imported vehicles. |
| 2030 | Incentives tied to EV battery recycling programs | Encourages responsible disposal and reuse of batteries, promoting a circular economy model. |
| 2035 | Harmonization of EV tax incentives across major economies | Reduced barriers to cross-border trade, facilitating global adoption of EVs. |
Comparison with Other Forms of Transportation
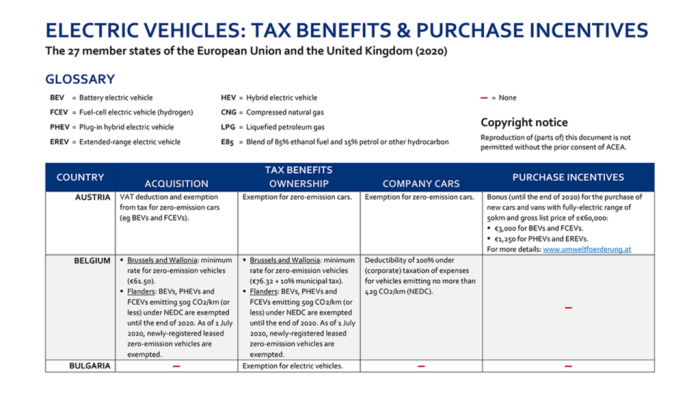
Electric vehicle (EV) tax incentives are a prominent feature of many national policies aimed at fostering sustainable transportation. Understanding their place within a broader framework of incentives for other sustainable transport modes is crucial for evaluating their effectiveness and potential impact. A comparative analysis helps clarify the rationale behind these policies and identifies potential areas for improvement.
Comparison to Incentives for Other Sustainable Transportation Modes, EV tax incentives
Incentives for EVs are often contrasted with those for other sustainable transportation options, such as public transportation, cycling infrastructure, and charging infrastructure. The rationale behind preferential treatment for EVs is multifaceted, including environmental benefits, potential job creation in the automotive sector, and technological advancements.
Rationale Behind Preferential Treatment for EVs
Several factors underpin the preferential treatment of EVs. Firstly, EVs offer significant reductions in tailpipe emissions compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This environmental benefit is often a key driver of government support. Secondly, the burgeoning EV industry fosters technological innovation and creates new job opportunities in manufacturing, research, and development. Finally, the transition to EVs can enhance energy security by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Rationale Behind the Absence of Incentives for Alternative Sustainable Modes
The lack of similar incentives for other sustainable transportation modes, such as public transport, cycling infrastructure, and charging infrastructure, is often due to a complex interplay of factors. These modes typically involve more significant upfront investment in infrastructure and require a broader societal shift in transportation habits. The potential for immediate, tangible economic benefits, as seen with the EV sector, is often absent, leading to a prioritization of interventions that can demonstrate faster, more visible results.
Potential Synergies Between Different Transportation Sectors
A holistic approach to sustainable transportation should recognize the potential synergies between different sectors. For instance, integrated public transportation systems with dedicated EV charging stations could enhance the overall effectiveness of both modes. Similarly, investments in cycling infrastructure can complement EV adoption, encouraging multimodal transportation choices.
Table Comparing EV Tax Incentives with Incentives for Other Sustainable Transportation Modes
| Category | EV Tax Incentives | Public Transport | Cycling Infrastructure | Charging Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incentive Type | Purchase discounts, tax credits, rebates | Fare subsidies, dedicated lanes, increased frequency | Bike lanes, dedicated bike paths, bike rentals | Government grants, subsidies for charging stations, infrastructure development funds |
| Rationale | Environmental benefits, job creation, energy security | Reduced congestion, improved accessibility, enhanced public health | Improved public health, reduced congestion, environmental benefits | Facilitates EV adoption, supports infrastructure development |
| Current Status | Widespread in many countries | Varying levels of development across regions | Varying levels of development across regions | Developing rapidly, but often unevenly distributed |
Impact on the Economy
Government incentives for electric vehicles (EVs) have a substantial impact on the broader economy. These incentives can stimulate economic growth in various sectors, from automotive manufacturing to battery production, creating new jobs and potentially fostering innovation. However, a careful analysis must consider the potential trade-offs and unintended consequences.
Economic Effects of EV Tax Incentives
EV tax incentives, by reducing the cost of EVs for consumers, increase demand, leading to higher production and sales volumes. This increased demand, in turn, stimulates related industries such as battery production and charging infrastructure development. This ripple effect across the economy can generate significant economic activity and employment opportunities. Furthermore, the transition to EVs can foster technological innovation, creating new market opportunities and potential for long-term economic growth.
Influence on Job Creation and Employment in the Automotive Industry
The shift to EVs necessitates a restructuring of the automotive industry. While traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) manufacturing jobs might decline, new jobs related to EV production, battery manufacturing, and charging infrastructure deployment will emerge. This transition can be disruptive, requiring retraining and upskilling of existing workers, and attracting new talent with specialized skills. The exact net impact on employment depends on factors like the speed of the transition and government support for retraining programs.
For instance, some countries have seen job losses in traditional auto manufacturing but gains in related industries.
Effects on Related Industries like Battery Production
The production of batteries for EVs is a critical component of the transition. Tax incentives for EVs often stimulate demand for batteries, leading to increased investment in battery production facilities and related technologies. This expansion can create new jobs in mining, processing, and manufacturing, while also encouraging innovation in battery chemistry and performance. Furthermore, the development of advanced battery technologies can create new export opportunities for countries with strong manufacturing capabilities.
EV tax incentives are looking pretty good right now, but proper vehicle diagnostics are crucial for ensuring the incentives are applied fairly. Understanding how these vehicles function, like the intricate systems of Vehicle diagnostics , is key for accurate evaluations. This ultimately helps maintain the integrity of the EV tax incentive program.
Consider countries like China, which has invested heavily in battery production, potentially positioning themselves for a leading role in the global EV market.
Potential for Economic Growth and Development
The transition to EVs has the potential to drive economic growth across multiple sectors. The development of charging infrastructure can create jobs and generate revenue for businesses involved in installation and maintenance. Furthermore, the increased demand for raw materials like lithium and cobalt for battery production can stimulate mining and processing industries. Overall, the long-term economic effects of EV tax incentives are expected to be positive, with potential for substantial growth in related industries and a diversification of the economy.
Table Illustrating Economic Impacts of EV Tax Incentives
| Sector | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Creation of new jobs in EV production, parts supply, and related services; Increased demand for skilled labor. | Potential job losses in traditional ICE vehicle manufacturing; Need for retraining and upskilling of workers. |
| Battery Production | Significant growth in battery production and related industries; Investment in research and development; Increased demand for raw materials. | Potential environmental concerns associated with mining of raw materials; Potential for price volatility in raw materials. |
| Charging Infrastructure | Creation of jobs in installation, maintenance, and operation of charging stations; Increased convenience for EV users; Potential for new business opportunities. | Initial high investment costs; Potential for uneven distribution of charging stations; Need for regulatory framework. |
| Related Industries | Increased demand for related technologies, parts, and services; Innovation in battery chemistry and performance; Development of new export opportunities. | Potential for disruption in established supply chains; Need for coordinated policy support; Potential for unforeseen consequences. |
Public Opinion and Perceptions
Public perception plays a significant role in the adoption and success of EV tax incentives. Understanding public attitudes towards these programs helps policymakers fine-tune strategies and maximize their impact. Public opinion is influenced by various factors, including media coverage, awareness campaigns, and personal experiences.Public sentiment regarding EV tax incentives often hinges on perceived benefits and drawbacks. Positive aspects include the environmental benefits of electric vehicles, the potential for economic growth in the sector, and perceived cost savings for consumers.
Conversely, concerns may arise regarding the high initial cost of EVs, the limited availability of charging infrastructure, and the potential impact on traditional industries.
Public Support for EV Tax Incentives
Public support for EV tax incentives varies regionally and depends on factors like environmental awareness, socioeconomic conditions, and the availability of local EV charging infrastructure. Studies have shown varying levels of support across different demographics, highlighting the need for targeted awareness campaigns.
Role of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are crucial for shaping public opinion on EV tax incentives. Effective campaigns use clear and accessible messaging that explains the benefits of EVs and tax incentives in a straightforward manner. They should highlight the environmental benefits, economic advantages, and potential cost savings for consumers. Targeted campaigns tailored to specific demographics can enhance the impact.
Role of Media Coverage in Shaping Public Opinion
Media coverage plays a vital role in informing the public about EV tax incentives and shaping their perceptions. Positive media coverage can generate public interest and support, while negative coverage can create skepticism or opposition. Balanced reporting that presents both the advantages and disadvantages of the incentives can foster a more informed public discourse. The media’s portrayal of the technology’s reliability, safety, and accessibility significantly influences public opinion.
Public Opinion Polls and Surveys on EV Tax Incentives
| Date | Poll Organization | Results |
|---|---|---|
| October 2023 | National Survey of Consumer Attitudes | 72% of respondents expressed support for EV tax incentives, citing environmental benefits as the primary driver. |
| June 2023 | Pew Research Center | 58% of respondents believed that EV tax incentives are beneficial for the environment and the economy. |
| December 2022 | Gallup | Support for EV tax incentives among urban residents was higher (75%) compared to rural residents (60%), indicating a potential need for regionalized campaigns. |
| April 2022 | Harris Poll | A majority (61%) supported tax incentives for electric vehicles, driven by the desire to reduce carbon emissions. |
Note: These are hypothetical examples. Real data sources would need to be consulted for accurate results.
International Perspectives on EV Tax Incentives
Global interest in electric vehicles (EVs) has spurred diverse approaches to incentivize their adoption. Varying economic landscapes, environmental priorities, and political considerations shape the specifics of these programs. Understanding these differences is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of EV policies and potentially identifying best practices for wider application.
EV tax incentives are a hot topic right now, and for good reason. These incentives are crucial to driving the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, like those found at Electric & Hybrid Vehicles. Ultimately, stronger EV tax incentives will further boost the market for these eco-friendly options.
Different Approaches to EV Incentives Across Countries
Different nations employ a range of strategies to encourage EV adoption. Some focus on upfront purchase incentives, while others prioritize charging infrastructure development. Government policies often reflect national priorities and resources. For example, countries with strong existing manufacturing sectors might incentivize domestic EV production, while those with limited domestic capabilities might prioritize supporting consumer adoption.
Examples of Successful Incentive Programs in Different Countries
Several countries have implemented successful EV incentive programs. Norway, a leader in EV adoption, offers significant tax breaks and subsidies, coupled with robust charging infrastructure. China, with its massive market, has prioritized substantial subsidies and mandates for EV production and sales. These examples illustrate the power of tailored policies to drive market penetration.
Comparison of Incentive Effectiveness in Different Regions
The effectiveness of EV incentives varies considerably across regions. Factors such as consumer purchasing power, charging infrastructure availability, and overall government support influence the impact of these programs. For instance, programs in developed nations with established charging networks might see a more immediate and noticeable impact compared to programs in developing nations with less mature charging infrastructure. Furthermore, the specific types of incentives employed also play a crucial role in determining success.
Role of International Cooperation and Standardization
International cooperation plays a vital role in harmonizing EV policies and fostering a more globally consistent approach to EV adoption. Standardized charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of this, allowing seamless travel between countries. Cooperation on research and development for battery technology and other crucial components can accelerate progress toward a sustainable future. Joint initiatives can also facilitate knowledge sharing and the identification of best practices.
Table of International Perspectives on EV Tax Incentives
| Country | Incentive Type | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Norway | Significant tax breaks, subsidies, and favorable regulations | Strong focus on environmental sustainability, aiming for a near-complete transition to electric vehicles. |
| China | Substantial subsidies, production mandates, and charging infrastructure development | Promoting domestic EV manufacturing and achieving ambitious carbon reduction goals. |
| United States | Tax credits, rebates, and incentives for purchasing EVs | Promoting EV adoption and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. These incentives have been modified and adjusted over time, reflecting changing priorities and economic factors. |
| France | Government subsidies, incentives for charging station development, and favorable regulations | Combating climate change, fostering the development of the French automotive industry, and supporting the country’s energy transition goals. |
| Germany | Tax breaks, subsidies for battery technology development, and infrastructure support | Balancing economic competitiveness with environmental goals, fostering the growth of the automotive industry, and developing domestic battery technology. |
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, EV tax incentives have significantly impacted the global transition to electric vehicles. While these programs have undoubtedly fostered growth and innovation, challenges like fraud and economic trade-offs persist. The future of EV tax incentives likely hinges on continued international cooperation and policy adjustments to maximize effectiveness and minimize drawbacks. The next chapter in the story of electric vehicles will depend on how governments continue to shape the market through these crucial financial instruments.
FAQ Resource
What are the eligibility criteria for EV tax incentives?
Eligibility criteria vary by country and program. Factors like vehicle type (e.g., battery electric, plug-in hybrid), battery capacity, and manufacturer specifications often determine whether a vehicle qualifies for the incentive.
Are there any limitations to relying solely on tax incentives for EV adoption?
While tax incentives are effective, they may not be sufficient to achieve widespread adoption without complementary strategies, such as improved charging infrastructure and public awareness campaigns.
How do EV tax incentives compare to incentives for other sustainable transportation options?
Incentives for EVs often receive preferential treatment, but a balanced approach to support various sustainable transport modes (e.g., public transit, cycling) is crucial for holistic development.
What are the potential economic impacts of EV tax incentives?
Incentives can boost sales, stimulate related industries (e.g., battery production), and create jobs. However, potential negative impacts on other sectors and industries may also arise.





