Charging at home offers a convenient and cost-effective alternative to public charging stations. This guide delves into the various aspects of home charging, from choosing the right equipment to maximizing energy efficiency.
We’ll explore different charging options, installation procedures, cost comparisons, safety considerations, and the latest trends in home charging technology. Understanding these details is key to making an informed decision about your charging needs.
Home Charging Infrastructure
Home charging infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). Different options cater to various needs and budgets, ranging from convenient portable chargers to sophisticated, integrated wallbox systems. Understanding the nuances of each method allows EV owners to make informed decisions aligning with their individual circumstances.
Home Charging Options
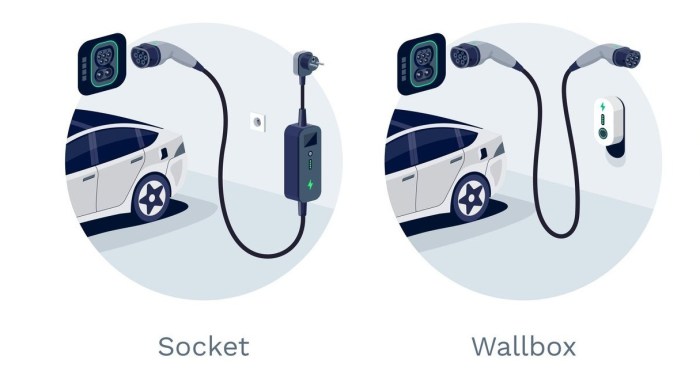
Various home charging solutions cater to different needs and budgets. These options include portable chargers, wallboxes, and more sophisticated charging stations. The choice depends on factors such as charging speed requirements, installation complexity, and budget constraints.
Wallboxes
Wallboxes are integrated charging stations installed directly into the home’s electrical system. They offer a significant advantage in terms of charging speed, typically exceeding portable chargers and sometimes even public charging stations. Installation involves professional electricians and careful consideration of electrical requirements, potentially necessitating upgrades to the home’s existing electrical infrastructure. This process can be time-consuming but results in a reliable and efficient charging solution.
Portable Chargers
Portable chargers are a more budget-friendly alternative, often smaller and more easily transported than wallboxes. They plug into a standard household outlet, providing a convenient way to top up the vehicle’s battery. However, their charging speed is considerably slower compared to wallboxes, often taking several hours to fully charge the vehicle. This option is ideal for occasional charging or for users with limited budget or charging needs.
Electrical Requirements
The electrical requirements for each charging station vary significantly. Wallboxes necessitate specialized circuits and potentially larger amperage capacity than portable chargers. Portable chargers utilize standard household outlets, which are less demanding on the home’s electrical system. Understanding these differences is crucial to ensure safe and effective installation.
Comparison of Home Charging Solutions
| Charging Method | Cost | Installation Time | Charging Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wallbox | High (typically $1,500 – $5,000) | Medium (1-3 days, depending on complexity) | High (typically 30-60 minutes for a full charge) |
| Portable Charger | Low (typically $200 – $500) | Low (typically 1-2 hours) | Low (typically 6-12 hours for a full charge) |
| Charging Station | Medium (typically $500 – $2,000) | Medium (1-3 days) | Medium (typically 2-4 hours for a full charge) |
Note
Costs and times are estimates and may vary depending on specific models, installation complexity, and location.*
Installation and Setup
Installing a home charging station requires careful planning and execution to ensure safety and proper functionality. This process involves understanding local regulations, electrical requirements, and safety procedures. A well-installed charging station will provide a reliable and convenient charging solution for your electric vehicle.Proper installation is crucial for the safe and effective operation of a home charging station. This involves adhering to electrical codes, ensuring sufficient amperage, and implementing safety measures to prevent hazards.
Following a structured installation process and utilizing appropriate safety measures will guarantee a safe and efficient charging experience.
Necessary Permits and Electrical Work
Understanding local building codes and obtaining necessary permits is a critical first step. Regulations vary significantly by region, so consulting with local authorities is essential. This involves verifying the permitted amperage and electrical specifications for your home and charging station. Compliance with local codes is vital to ensure the installation is legal and safe.
- Permitting: Contact your local building department or utility company to inquire about the specific requirements for installing an electric vehicle charging station. This process may involve submitting applications, providing documentation, and scheduling inspections. Failure to comply with local regulations could result in delays or rejection of the installation.
- Electrical Inspection: A qualified electrician must perform a thorough inspection to ensure the electrical wiring and circuits can safely support the charging station. This includes checking the amperage, voltage, and wiring capacity of the electrical panel to ensure that it can handle the additional load without overloading or overheating. The electrician will assess the existing wiring to determine its suitability and recommend any necessary upgrades or replacements.
This inspection is crucial to avoid electrical hazards and ensure long-term safety.
Safety Precautions
Safety should be paramount throughout the installation process. Proper grounding, surge protection, and appropriate circuit breakers are essential components. This minimizes the risk of electrical shock, fire, and other potential hazards. Using high-quality materials and adhering to established safety guidelines is vital to prevent future problems.
- Grounding: Ensuring proper grounding is crucial to prevent electrical shocks. The charging station’s grounding system should be connected to the building’s grounding system to provide a safe path for electrical current in case of faults. This will protect both the charging station and the user.
- Surge Protection: Installing surge protection devices (SPDs) helps shield the charging station and your vehicle from voltage fluctuations or surges that can damage sensitive electronic components. This will prevent potential damage to the charging station and connected devices, including the electric vehicle.
- Circuit Breakers: Using appropriate circuit breakers is critical to protect against overloads and short circuits. A dedicated circuit for the charging station is recommended to isolate the charging process and prevent potential hazards.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
A methodical approach to installation and setup minimizes potential errors and maximizes the efficiency of the process. This involves connecting the charging station to the power supply and the vehicle. Proper connections and procedures are critical for optimal charging performance.
- Power Supply Connection: Carefully connect the charging station’s power cable to the designated circuit breaker. Ensure a secure connection to prevent loose wiring and potential fire hazards. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific wiring procedures.
- Vehicle Connection: Connect the charging cable to the vehicle’s charging port. Ensure the cable is securely plugged into both the charging station and the vehicle. Pay close attention to the visual indicators to confirm proper connection and functionality.
- System Verification: Verify that the charging station is functioning correctly. Check the charging status on the station’s display or the vehicle’s onboard system to ensure proper power flow. Monitor the charging process for any unusual behavior, such as overheating or malfunctioning of the station. This ensures that the charging process is taking place correctly.
Installation Flowchart
A visual flowchart illustrates the installation process for a typical home charging station. This visual representation clarifies the sequence of steps involved in the process.[Note: A flowchart, as requested, cannot be included here in HTML plaintext format. A flowchart would be a diagram, not text.]
Charging Costs and Benefits: Charging At Home
Home charging offers a compelling alternative to public charging stations, presenting a range of cost-effective and environmentally conscious advantages. The upfront investment in a home charging setup can be offset by significant long-term savings.Understanding the comparative costs and benefits is crucial for making an informed decision. Factors such as electricity rates, charging time, and potential incentives play a significant role in the overall financial and environmental impact of home charging.
Comparing Home and Public Charging Costs
Electricity rates vary significantly by region and utility provider. For instance, a household in California might experience different electricity costs compared to a household in Texas. The cost of charging at home is directly linked to the electricity rate and the duration of the charging session. A longer charging session at a lower electricity rate could still be more economical than a shorter charging session at a higher electricity rate.Public charging stations, while offering convenience, often come with higher costs per kilowatt-hour (kWh) charged.
Furthermore, charging times at public stations can be considerably longer than at home, depending on the availability of charging ports and the station’s capacity. The additional time spent waiting at a public station translates into a greater cost, even if the per-kWh rate is lower.
Environmental Benefits of Home Charging
Home charging significantly reduces reliance on public charging infrastructure, minimizing the strain on the overall charging network. This reduction in demand for public stations translates to lower environmental impact associated with the construction and operation of additional charging infrastructure.Home charging also reduces the need for frequent trips to public charging stations. This decrease in travel reduces the emission of greenhouse gases and contributes to a smaller carbon footprint.
Savings on Fuel Costs
Home charging can directly translate to savings on fuel costs, especially for drivers of electric vehicles (EVs). Instead of filling up gas tanks, EV owners can rely on the convenience of charging at home, potentially saving hundreds of dollars annually.For example, an EV driver who commutes 50 miles per day and charges at home could save significantly on fuel costs compared to someone who charges exclusively at public stations.
Incentives and Rebates for Home Charging
Numerous incentives and rebates are available to encourage the adoption of home charging infrastructure. These programs often cover part of the installation costs, potentially making the transition to home charging more accessible.
- Government programs: Many governments offer financial incentives for the installation of home charging stations, often in the form of tax credits or rebates. The specific amounts and eligibility criteria vary by location and program.
- Utility companies: Some utility companies provide incentives or rebates for installing home charging stations, potentially lowering the overall cost of installation. These programs may include reduced electricity rates or financial contributions towards equipment.
- Local governments: Local governments might offer programs to support the development of sustainable transportation options. This could include rebates or grants for the installation of home charging stations.
Vehicle Compatibility
Home charging solutions are becoming increasingly popular, but the availability and suitability of these systems vary across different vehicle types. Understanding the compatibility of your vehicle with various charging standards is crucial for a seamless and effective charging experience. This section details the different vehicle types compatible with home charging stations, the charging standards and connectors used, and the process for determining and implementing compatibility.
Identifying Compatible Vehicle Types
Electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) are the primary types compatible with home charging stations. Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) rely solely on electricity for power, while PHEVs combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, allowing for some electric-only driving. The charging infrastructure required for these vehicles is largely similar, focusing on the charging connector and the charging standards.
Charging Standards and Connectors
Different charging standards and connectors are employed for different vehicle types. The most common home charging standard is Level 2, utilizing a 240-volt AC charging system. This standard is widely supported by various EV and PHEV models. Level 2 charging is generally sufficient for home charging and provides a balance between charging speed and cost-effectiveness. Level 1 charging is a lower-power AC charging standard often found in standard household outlets, but is significantly slower.
Level 3 (DC fast charging) is typically reserved for public charging stations due to its higher power output and speed, and is not commonly found in home charging setups.
Determining Vehicle Support for Home Charging
A straightforward method to determine your vehicle’s compatibility with home charging is to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual. The manual will detail the specific charging connectors supported by your model, including the charging port type (e.g., CCS, CHAdeMO, Type 2). Many modern EVs and PHEVs are equipped with a Type 2 connector, which is commonly used for Level 2 home charging.
Alternatively, online resources and forums dedicated to electric vehicles often have detailed information about specific vehicle models and their charging capabilities.
Connecting a Home Charging Station to Your Vehicle
The connection process for a home charging station to a specific vehicle model varies slightly based on the charging station and vehicle model, but generally follows a similar pattern. First, ensure the home charging station is correctly installed and wired in accordance with local electrical codes. Next, verify the charging cable compatibility with both the charging station and the vehicle.
The cable should precisely fit both the charging station’s output port and the vehicle’s charging port. Finally, connect the charging cable to both the charging station and the vehicle. Observe the charging indicator lights on both the charging station and the vehicle to confirm a successful connection. Following these steps ensures a safe and efficient charging experience.
Example: Connecting a Tesla Model 3 to a Level 2 Home Charging Station
The Tesla Model 3, for example, uses a CCS connector. A Level 2 home charging station with a compatible CCS-to-Type 2 adapter is needed for home charging. The adapter allows the station’s Type 2 output to be compatible with the vehicle’s CCS input. Once connected, the charging process begins, with the charging station’s display and the vehicle’s dashboard providing charging status updates.
Smart Charging and Energy Management
Smart charging, a key feature of modern electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure, allows for the optimization of energy usage and electricity costs. This dynamic approach goes beyond simply plugging in and charging; it intelligently manages the charging process to benefit both the vehicle owner and the broader energy grid. By integrating various factors, smart charging systems aim to reduce peak demand, promote renewable energy integration, and lower electricity bills.Smart charging systems intelligently adjust the charging rate of EVs based on real-time energy pricing, grid conditions, and vehicle needs.
This approach offers numerous benefits, not only for individual users but also for the stability and efficiency of the overall power system. It allows for the integration of renewable energy sources, leading to a more sustainable energy future.
Smart Charging Benefits
Smart charging offers a multitude of benefits. It can significantly optimize energy usage by considering factors like time-of-use electricity pricing, renewable energy availability, and grid load. This proactive approach can lead to substantial cost savings for EV owners.
Smart Charging Technologies
Various smart charging technologies exist, each with its unique features and benefits. Some prominent examples include:
- Time-of-Use (TOU) Charging: This technology enables charging at times when electricity prices are lower, often during off-peak hours. By strategically scheduling charging sessions, EV owners can minimize their electricity costs, aligning charging with cheaper energy rates. For example, a home charging system with TOU capabilities can schedule charging during the night when electricity rates are lower, potentially saving significant costs over time.
- Grid-Based Charging: This advanced technology enables communication between the charging station and the power grid. This allows the charging station to respond to grid-level needs, such as balancing load or supporting renewable energy sources. This system prioritizes grid stability, promoting a more sustainable energy infrastructure.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Charging: This innovative technology enables EVs to act as a source of energy for the grid, not just consumers. During periods of high energy demand or low renewable energy generation, EVs can discharge power back into the grid. This bidirectional energy flow can improve grid stability and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Smart Charging Optimization Diagram
The following diagram illustrates how a smart charging system can optimize energy consumption:
(Insert a diagram here. The diagram would show a simplified representation of the smart charging system with connected elements like the EV, home charging station, energy grid, and a central control system. Arrows would show the flow of data and energy between these components. The diagram would visually depict how the charging station receives data about grid conditions, energy prices, and the EV’s battery level. Based on this data, the charging station adjusts the charging rate to optimize energy usage and reduce costs. The system could be further elaborated to include time-of-use pricing data and renewable energy availability.)
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintaining your home charging equipment is crucial for its longevity and safe operation. Regular upkeep minimizes the risk of malfunctions and ensures optimal charging performance for your electric vehicle. Proper troubleshooting steps are vital for quickly identifying and resolving charging issues, preventing potential safety hazards.Understanding potential problems and how to address them promptly will save time and money in the long run.
By following preventative maintenance routines and troubleshooting guides, you can maximize the lifespan of your home charging system and enjoy a reliable charging experience.
Maintenance Tasks for Home Charging Equipment, Charging at home
Regular maintenance is key to preventing potential issues with your home charging station. This involves inspecting and cleaning components, checking connections, and ensuring the equipment is operating within safe parameters.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the charging station for any visible signs of damage, such as frayed wires, loose connections, or corrosion. Check for damage to the enclosure or surrounding area, which may indicate underlying problems.
- Cleaning: Clean the charging station’s exterior and components with a soft, damp cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the equipment. Ensure the charging port and surrounding areas are free of debris.
- Connection Checks: Verify all electrical connections are secure and properly tightened. Look for any signs of looseness, corrosion, or damage to the wiring. This proactive step is essential for safety and performance.
- Grounding Verification: Regularly check the grounding connections to ensure they are intact and properly connected to the ground. A faulty grounding system can lead to electrical hazards.
- Software Updates (if applicable): Keep the charging station’s software updated to benefit from improved functionality and security enhancements. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for details on how to update the software.
Troubleshooting Charging Issues
Troubleshooting charging problems can often be resolved with simple checks and adjustments. Identifying the root cause is crucial to effective troubleshooting.
Charging your vehicle at home is super convenient, especially for those considering a switch to electric or hybrid vehicles. Choosing between a hybrid and an electric car often hinges on factors like charging infrastructure and personal needs, as detailed in this comparison: Hybrid vs electric. Ultimately, home charging offers a flexible and affordable solution for both types of vehicles, making it a key factor in the decision-making process.
- Slow Charging: If the charging speed is significantly slower than expected, first check the electrical outlet for proper power. Ensure the outlet has sufficient amperage capacity. Verify the vehicle is compatible with the charging station and that the charging cable is in good condition. A malfunctioning charging station or cable can also be a cause.
- Charging Errors: Charging errors can stem from various factors. Verify the vehicle is correctly connected to the charging station. Check for obstructions in the charging port. If the issue persists, consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide for specific instructions.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Home Charging Equipment
Proactive maintenance plays a crucial role in prolonging the life of your charging station.
- Regular Maintenance Schedule: Establish a routine for performing visual inspections, cleaning, and connection checks to proactively address potential issues. Consistency is key.
- Environmental Protection: Protect the charging station from extreme temperatures, moisture, and dust to avoid premature deterioration. Ensure the charging station is installed in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Overloading Prevention: Avoid overloading the charging station by ensuring the combined charging demand of multiple vehicles doesn’t exceed its capacity. This prevents overheating and damage to the equipment.
Checking Electrical Connections for Hazards
Electrical safety is paramount when working with home charging equipment.
- Proper Grounding: Ensure the charging station and its associated wiring are correctly grounded to prevent electrical shocks. This crucial step is essential for safety.
- Visual Inspection of Wiring: Inspect all wiring for any signs of damage, such as exposed wires, cuts, or fraying. Look for loose connections or corrosion on the wires.
- Professional Assistance: If you encounter any uncertainty or difficulty during the inspection process, seek assistance from a qualified electrician. Electrical work should always be performed by a professional to ensure safety and compliance with electrical codes.
Safety Considerations
Home EV charging, while convenient, requires careful attention to safety precautions. Proper installation and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial to prevent accidents and ensure the longevity of your charging system. Understanding the inherent safety features of charging stations and potential hazards is vital for a safe and worry-free charging experience.Careful consideration of electrical safety measures, particularly when dealing with high-voltage systems, is paramount.
This includes not only the charging equipment itself but also the surrounding environment and potential interactions with other electrical appliances. Electrical safety is paramount to prevent fire hazards, electrical shocks, and other potential accidents.
Importance of Safety Precautions
Properly installed and maintained home charging systems minimize the risk of electrical hazards. Following manufacturer instructions and local electrical codes is crucial. Safety precautions protect both the user and the property. Ignoring safety measures can lead to significant risks, including electrical shocks, fires, and equipment damage.
Safety Features in Charging Stations
Various safety features are built into modern EV charging stations. These features are designed to mitigate risks associated with electrical hazards and ensure the safety of the user and the property.
- Grounding and Earthing: All charging stations are designed with proper grounding and earthing systems. This prevents the flow of current to unintended paths, reducing the risk of electrical shocks. Grounding and earthing systems are crucial in preventing electrical hazards.
- Overcurrent Protection: Circuit breakers and fuses are vital safety components in EV charging stations. They automatically interrupt the flow of electricity if there’s an overload, preventing fires and electrical damage. Overcurrent protection is a fundamental safety measure in any electrical system.
- Over-temperature Protection: Advanced charging stations are equipped with temperature sensors. These sensors detect overheating in the charging components and automatically shut off the charging process to prevent potential fires. Overheating is a common cause of equipment failure and fire hazards.
- Insulation and Enclosure: High-voltage components are properly insulated and enclosed in protective housings to prevent accidental contact with electricity. The enclosure protects the internal components and prevents electrical shocks.
Potential Safety Hazards and Mitigation
Recognizing and mitigating potential hazards is essential for safe home EV charging.
- Damaged or Worn Cables/Cords: Inspect charging cables and cords regularly for any damage or wear. Damaged cables can lead to electrical shorts and potential fires. Replacing damaged charging cables is crucial to maintain safety.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect installation of charging stations can create safety hazards. Ensure the installation complies with local electrical codes and the manufacturer’s instructions. Incorrect installation poses a significant safety risk.
- Improper Wiring or Connections: Check all wiring and connections for any loose or damaged components. This can lead to overheating and electrical hazards. Checking wiring and connections regularly is essential for safety.
- Water Exposure: Ensure that the charging station is not exposed to water or moisture. Water and electricity are a dangerous combination, potentially causing electrical shocks and equipment damage. Protect the charging station from water exposure.
Reporting Electrical Issues
Prompt reporting of electrical issues related to home charging is essential.
Home charging is becoming increasingly important for EVs, reflecting the growing adoption of electric vehicles within the broader Automotive industry. This trend highlights the need for readily available and convenient charging infrastructure, which in turn drives innovation in both the vehicle and charging station sectors. Ultimately, home charging is set to play a crucial role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
- Contacting Electricians: If you encounter any electrical issues, contact a qualified electrician immediately. They can diagnose the problem and ensure safe repairs. Professional electricians are equipped to handle electrical issues related to home charging.
- Following Manufacturer Instructions: Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for reporting procedures. Manufacturers have specific guidelines for handling electrical problems related to home charging.
- Documentation: Document the issue, including the date, time, and any relevant details. This information will be helpful for troubleshooting and repair. Proper documentation is essential for troubleshooting and repair.
- Local Electrical Codes: Ensure that any repairs comply with local electrical codes and regulations. Adherence to local codes is essential for safety.
Future Trends in Home Charging
Home charging infrastructure is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in battery technology, energy storage, and smart home integration. These advancements are promising a future where home charging is not only more convenient but also more efficient and environmentally friendly. Predicting the exact trajectory of these developments is challenging, but examining current trends and emerging technologies offers valuable insight into the possibilities.The future of home charging will be characterized by a significant shift towards smarter, more integrated systems.
This evolution will not only impact the charging process itself but also the overall energy management within a household. This integration will enhance convenience and potentially lower energy costs, alongside reduced environmental impact.
Charging Speeds and Efficiency
Current home charging speeds, while adequate for many, are anticipated to increase substantially. The development of faster charging technologies, like advanced DC fast charging, is a significant area of focus. These advancements will reduce the time needed to fully charge an electric vehicle (EV), potentially cutting down charging time from hours to minutes. Higher efficiency in the charging process itself is also a key focus.
Improvements in charging circuitry and energy conversion can reduce energy losses, leading to a more economical and sustainable charging experience. A prime example of this efficiency is the use of more efficient inverters and transformers that minimize energy loss during conversion.
Integration with Smart Home Systems
Home charging systems are increasingly integrating with broader smart home ecosystems. This integration enables dynamic energy management, optimizing charging schedules based on factors such as energy prices, renewable energy generation, and household electricity needs. This integration can allow for more efficient use of renewable energy sources, such as solar power, and optimize the charging schedule to align with peak demand reduction periods, leading to lower electricity costs and a reduced carbon footprint.
For example, a smart home system can detect when solar panels are producing excess energy and prioritize charging during those periods.
Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize home charging. One such technology is the utilization of advanced battery management systems (BMS) that can optimize charging profiles based on the battery’s specific characteristics and charging requirements. This personalized approach can maximize battery lifespan and performance. Furthermore, advancements in wireless charging technologies, like inductive charging, could eliminate the need for physical cables, potentially enhancing aesthetic appeal and convenience.
Another area of innovation is the development of modular charging stations that can adapt to evolving EV needs, providing future-proof charging solutions.
Comparison with Current Methods
Current home charging methods, primarily relying on AC charging, will be contrasted with future advancements. The introduction of faster DC charging capabilities will drastically reduce charging times, potentially making them comparable to filling a gasoline tank. The integration of smart home systems will lead to dynamic charging optimization, unlike the static schedules of current systems. Future systems will not only focus on charging but also on managing the entire household’s energy consumption, leading to a much more integrated and efficient energy management system.
Comparison with Other Charging Methods
Home charging offers a compelling alternative to public charging stations, particularly for frequent drivers. Understanding the trade-offs between these two options is crucial for making an informed decision. This comparison will highlight the key advantages and disadvantages of each method, aiding in the selection of the most suitable charging solution.
Cost Comparison
Home charging typically proves more economical in the long run. While initial installation costs may be involved, ongoing expenses are significantly lower than relying on public charging stations. The cost of electricity, factored against the rate of public charging, usually favors home charging, especially for frequent users. For example, a typical household electricity cost of $0.15 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) compared to a public charging station rate of $0.50 per kWh would illustrate this difference.
Convenience and Accessibility
Home charging boasts unparalleled convenience, allowing drivers to charge their vehicles whenever and wherever it’s most convenient, without the need for planning trips to public charging stations. This eliminates the need for searching for available charging points or waiting in queues, ensuring a smooth charging experience. Conversely, public charging stations can be scattered geographically, and availability can vary depending on location and time.
The availability of charging points is an important factor, particularly in areas with limited public charging infrastructure.
Pros and Cons of Different Charging Methods
| Charging Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Home Charging | Cost-effective in the long run, convenient, flexible charging schedule, avoids public charging station limitations. | Initial investment for installation, requires dedicated electrical infrastructure, limited charging capacity if not upgraded. |
| Public Charging Stations | Convenient for occasional drivers, accessible in various locations, provides backup charging options. | Charging costs are typically higher than home charging, potential waiting times and limited availability, requires planning and searching for stations. |
Factors Influencing Charging Method Choice
Several factors influence the optimal charging strategy. The frequency of driving, the availability of home charging infrastructure, and the cost of electricity all play a significant role. Individuals who drive frequently and have readily available home charging options will likely prefer home charging. In contrast, occasional drivers or those in areas with limited home charging access may find public charging stations more practical.
Geographic location, access to charging stations, and individual driving habits further influence the decision-making process.
Key Differences Between Home and Public Charging
Home charging generally offers a more cost-effective and convenient solution for frequent drivers with dedicated charging infrastructure. Public charging stations provide a supplementary option for occasional drivers or those in areas with limited home charging access. The key difference lies in the balance between cost, convenience, and accessibility, leading to distinct advantages and disadvantages. A careful assessment of individual needs and circumstances is vital for making the optimal choice.
Last Point

In conclusion, charging at home presents a compelling solution for EV owners seeking a reliable, affordable, and eco-friendly charging experience. By understanding the available options, installation processes, and potential benefits, you can confidently integrate home charging into your daily routine.
FAQ Compilation
What are the different types of home charging stations?
Common options include wallboxes, portable chargers, and different types of charging stations, each with varying installation complexities, costs, and charging speeds.
How much does home charging typically cost compared to public charging?
Home charging often proves more economical, especially considering electricity rates and the time saved by not having to travel to public charging stations.
What safety precautions should I take when installing a home charging station?
Always ensure proper electrical work, adhere to safety guidelines, and consult with qualified professionals for installation to prevent any potential hazards.
Are there any incentives for installing a home charging station?
Various government and utility programs offer incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of home charging, reducing the initial investment.





